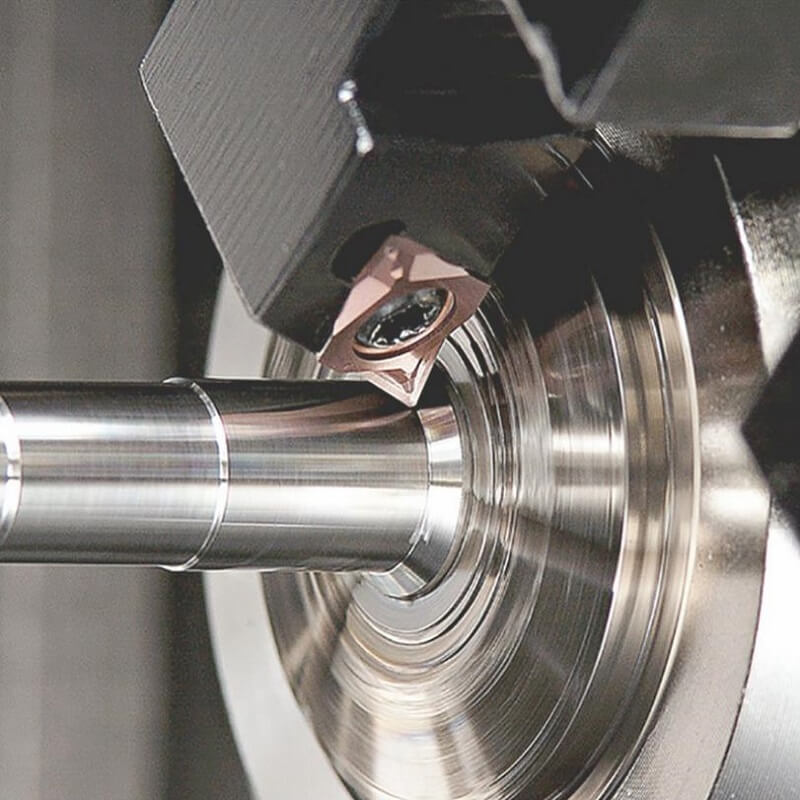
Turning and milling are two fundamental machining processes used in the manufacturing industry to shape and finish workpieces.
While both processes involve removing material from a workpiece, they differ in their approach, tooling, applications,
and cutting direction. Let's explore these differences in more detail.
Turning:
Turning is a machining process that involves rotating a workpiece while a cutting tool traverses along the surface of the rotating
workpiece. The cutting tool removes material to create the desired shape and dimensions. Key characteristics of turning include:
1. Operation:
- Workpiece Rotation: In turning, the workpiece is rotated on a lathe machine. The rotation can be continuous or intermittent,
depending on the desired shape and features.
- Stationary Cutting Tool: The cutting tool remains stationary while the workpiece rotates. It moves along the surface of the
workpiece, removing material to create the desired shape.
2. Tooling:
- Single-Point Cutting Tools: Turning primarily utilizes single-point cutting tools, such as lathe tools. These tools have a single
cutting edge and are mounted on a tool holder.
- Tool Holder: The cutting tool is fixed to a tool holder that allows for adjustment and replacement of tools as needed.
3. Applications:
- Cylindrical and Conical Shapes: Turning is commonly used to create cylindrical or conical-shaped workpieces, such as shafts,
spindles, and cylindrical surfaces.
- External and Internal Turning: External turning refers to removing material from the outer surface of the workpiece, while
internal turning involves removing material from internal surfaces, such as creating holes or cavities.
4. Cutting Direction:
- Parallel to Axis of Rotation: In turning, the cutting tool moves parallel to the axis of rotation of the workpiece. This results in
removing material along the radial direction, creating rotational symmetry.
Milling:
Milling is a machining process where a rotating multi-point cutting tool removes material from a stationary or moving workpiece.
Milling offers more versatility in terms of shapes and features that can be created. Key characteristics of milling include:
1. Operation:
- Rotating Multi-Point Cutting Tool: Milling utilizes multi-point cutting tools, such as end mills or face mills. These tools have
multiple cutting edges and are mounted on a rotating spindle.
- Workpiece Movement: In milling, the workpiece can remain stationary or move in different directions, depending on the desired
shape and features.
2. Tooling:
- Multi-Point Cutting Tools: Milling employs multi-point cutting tools that have multiple cutting edges. These tools come in
various shapes and sizes, allowing for a wide range of cutting possibilities.
3. Applications:
- Versatile Shape Creation: Milling is known for its versatility in creating different shapes and features, including flat surfaces, slots,
pockets, contours, and complex 3D geometries.
- Surface Finishing: Milling can also be used for surface finishing operations, such as creating smooth surfaces or adding texture.
4. Cutting Direction:
- Multiple Axes Movement: Milling allows the cutting tool to move along multiple axes, including the X, Y, and Z axes. This enables
the creation of intricate shapes and contours.
In summary, turning and milling are two distinct machining processes with their own characteristics and applications. Turning is ideal
for cylindrical or conical workpieces, while milling offers more versatility in shape creation and is suitable for a wider range of
workpiece geometries. Understanding the differences between these processes helps manufacturers select the most appropriate
method for their specific machining requirements.
Contact person: Steve Lee
E-mail: [email protected]
Phone: 86-731-22200908
Address: Floor 4,Building NO.15,Zhichuang Plaza,NO.1299,Liyu Road,Tianyuan District,Zhuzhou City, Hunan, P.R. CHINA
Tel:0086-19973342799
E-mail: [email protected]

WeChat Official Account